Have you ever noticed strange caterpillars munching on the leaves in your garden and wondered which ones might cause more damage? When it comes to protecting your trees and plants, knowing the difference between a Gypsy Moth Caterpillar and a Tent Caterpillar can save you time and frustration.
These two pests look similar but behave very differently—and your approach to managing them should too. Keep reading to discover how to spot each one, understand their habits, and take the right steps to keep your yard healthy and thriving.
Table of Contents
Appearance Traits
Appearance traits help us tell the Gypsy Moth Caterpillar and Tent Caterpillar apart. Each has distinct colors and body features. These details make identification easier in gardens or forests.
Understanding these traits can protect trees and plants from damage. Let’s look closer at their size, color, and markings.
Gypsy Moth Caterpillar Appearance
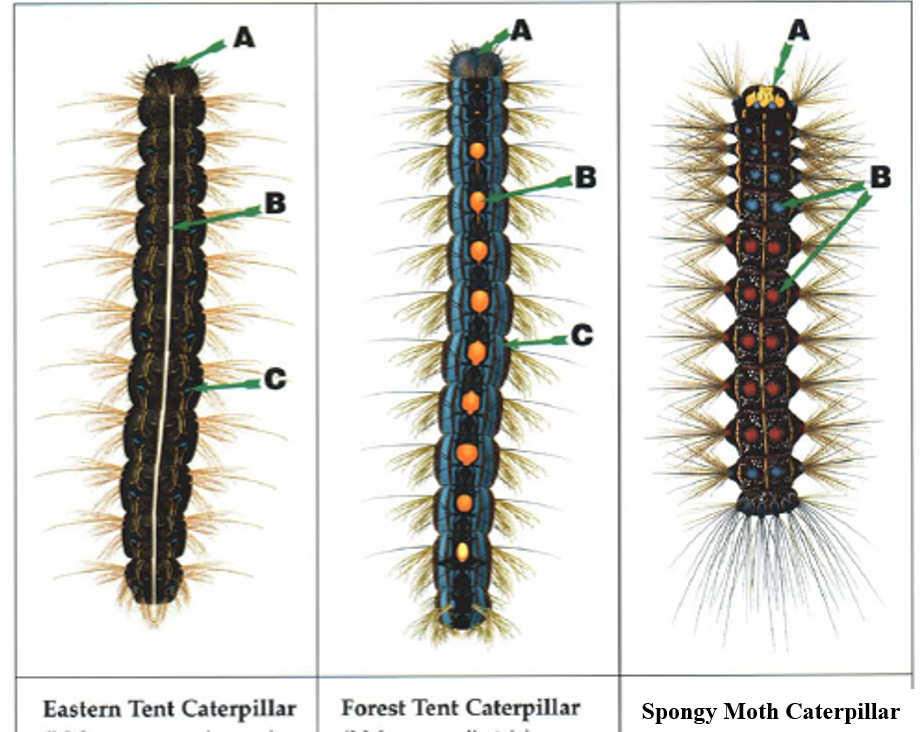
The Gypsy Moth Caterpillar is hairy and has a dark body. It usually measures about 2 to 3 inches long. A key sign is the row of blue and red dots along its back.
The hairs are long and thin, giving a fuzzy look. The head is brownish, and the body color varies from gray to black.
Tent Caterpillar Appearance
Tent Caterpillars are shorter, about 1.5 to 2 inches long. They have smooth bodies with bright markings. A white stripe runs down the center of their back.
The sides show blue and black patterns. Their heads are shiny and dark brown. They lack the hairy look of the Gypsy Moth Caterpillar.
Life Cycle Stages
The life cycle stages of the Gypsy Moth caterpillar and the Tent caterpillar differ in important ways. Understanding these stages helps identify each pest. Both go through four main stages: egg, larva, pupa, and adult. Each stage lasts different lengths of time. Their behaviors and appearance change at each stage.
Egg Stage
Gypsy Moth eggs appear in large, fuzzy clusters. They are tan or light brown. The clusters stick to tree bark or other surfaces. Eggs hatch in early spring after winter cold.
Tent caterpillar eggs are laid in tight bands around small branches. The eggs are shiny and dark brown. They stay on trees through winter. Eggs hatch just as leaves start to grow.
Larva (caterpillar) Stage
Gypsy Moth larvae are hairy with blue and red spots. They feed heavily on tree leaves. Larvae grow quickly and molt several times. They can strip trees bare if many are present.
Tent caterpillar larvae are smooth with a white stripe down the back. They live in silk tents built in tree branches. They eat leaves around their tents. Larvae also molt as they grow.
Pupa Stage
Gypsy Moth pupae form cocoons under loose bark or leaf litter. The pupa stage lasts about two weeks. During this time, the caterpillar changes into a moth.
Tent caterpillars pupate inside their tents or nearby. The pupa is inside a silk cocoon. This stage lasts about two to three weeks before moths emerge.
Adult Stage
Adult Gypsy Moths have tan wings with dark markings. Males fly well, but females cannot fly. Adults live only a short time to mate and lay eggs.
Adult Tent moths are smaller with dull brown wings. They fly at night. Females lay eggs on tree branches to start the cycle again.
Feeding Habits
Feeding habits reveal how Gypsy Moth caterpillars and Tent caterpillars affect trees. Both insects eat leaves but differ in their style and impact. Understanding these habits helps protect plants from damage.
Gypsy Moth Caterpillar Feeding Behavior
Gypsy Moth caterpillars eat leaves one by one. They prefer oak trees but eat many types of trees. They start feeding in spring and continue until they grow large. Their feeding can strip trees of leaves quickly.
They feed mostly during the day. The caterpillars climb up trees and chew the edges of leaves. This causes a ragged look on the leaves. Large groups of caterpillars can defoliate whole trees fast.
Tent Caterpillar Feeding Behavior
Tent caterpillars live in groups inside silk tents. They leave the tents to feed on leaves nearby. Their feeding happens mostly in the morning and evening. They prefer cherry, apple, and other fruit trees.
They eat whole leaves, leaving only the veins. This creates holes and skeletonized leaves. Tent caterpillars usually feed for a few weeks before turning into moths. Their group feeding can weaken trees but rarely kills them.

Habitat Preferences
Gypsy moth caterpillars and tent caterpillars live in different places. Each species chooses a habitat that suits its needs. Their habitat choice helps them survive and grow well.
Understanding where these caterpillars live helps control their spread. It also helps protect trees and plants from damage.
Gypsy Moth Caterpillar Habitat
Gypsy moth caterpillars prefer hardwood forests. They mostly live in oak, birch, and aspen trees. These trees give them food and shelter. They also thrive in urban areas with many trees.
They avoid wet or very cold places. Their eggs hatch in spring when leaves start to grow. Gypsy moths spread easily in large forested areas.
Tent Caterpillar Habitat
Tent caterpillars build silk tents in tree branches. They live mainly in cherry, apple, and crabapple trees. They like open woodlands and orchards. These areas provide plenty of food.
Tent caterpillars prefer trees that lose leaves in winter. They hatch early in spring. Their tents protect them from birds and bad weather.
Behavior Patterns
Behavior patterns reveal how insects act in their environment. These patterns help identify and manage pests like caterpillars. The Gypsy Moth Caterpillar and Tent Caterpillar show distinct behaviors. Understanding these can help protect trees and gardens.
Both caterpillars feed on leaves but differ in movement and shelter habits. These differences affect how they impact plants and how to control them.
Gypsy Moth Caterpillar Movement
Gypsy Moth Caterpillars move alone in search of food. They crawl slowly on tree trunks and branches. They do not build large communal nests. Their movement spreads damage over a wide area.
Tent Caterpillar Nesting Habits
Tent Caterpillars build silk tents in tree branches. They live together inside these tents. The nests protect them from predators and weather. They leave the tent to feed but return often.
Feeding Behavior Differences
Gypsy Moth Caterpillars eat leaves at night. They hide during the day under bark or leaves. Tent Caterpillars feed during the day outside their nests. They eat leaves quickly and in groups.
Response To Threats
Gypsy Moth Caterpillars drop from trees to escape danger. This helps them avoid birds and other predators. Tent Caterpillars stay inside their silk tents for safety. They rely on group defense to deter threats.
Impact On Trees
Both gypsy moth caterpillars and tent caterpillars affect trees, but their impact varies. Understanding how each one damages trees helps in managing them better. Trees can suffer from leaf loss, which weakens their growth and health.
Gypsy Moth Caterpillar Damage
Gypsy moth caterpillars eat large amounts of leaves quickly. They prefer oak trees but will eat many types. Heavy feeding can strip a tree bare in weeks. This leaf loss stops the tree from making food. Weakened trees become more open to diseases and other pests. Repeated defoliation can kill the tree over time.
Tent Caterpillar Damage
Tent caterpillars build silk tents in tree branches. They feed on leaves near their tents. Their damage is often less severe than gypsy moths. Trees usually recover after a tent caterpillar outbreak. Still, heavy infestations can slow tree growth. Young trees are more at risk from repeated feeding.
Comparing The Long-term Effects
Gypsy moths cause more long-term harm than tent caterpillars. Trees defoliated by gypsy moths often need years to recover. Tent caterpillar damage is usually temporary and less harmful. Both pests reduce tree vigor but at different levels. Monitoring and controlling these pests protects tree health.
Predators And Defenses
Predators and defenses shape the survival of Gypsy Moth Caterpillars and Tent Caterpillars. Both face many threats in the wild. They use different ways to protect themselves. Understanding these methods helps in managing their populations effectively.
Gypsy Moth Caterpillar Predators
Birds like cuckoos and blue jays eat Gypsy Moth Caterpillars. Small mammals, such as shrews, also hunt them. Parasitoid wasps lay eggs inside these caterpillars. The wasp larvae then feed on the host from within.
Gypsy Moth Caterpillar Defenses
Gypsy Moth Caterpillars have toxic hairs that irritate predators. Their colors warn animals they might be harmful. They can curl up to protect soft parts of their bodies. These defenses reduce attacks by many predators.
Tent Caterpillar Predators
Birds are the main enemies of Tent Caterpillars. Wasps and flies also parasitize their eggs and larvae. Small mammals like mice sometimes feed on their tents. These predators help keep Tent Caterpillar numbers in check.
Tent Caterpillar Defenses
Tent Caterpillars build silk tents to hide from predators. They stay inside during the day to avoid birds. Their bodies have irritating hairs to deter attackers. Group living offers extra protection through numbers.
Control Methods
Controlling Gypsy Moth caterpillars and Tent caterpillars requires different approaches. Both pests can damage trees and plants. Early action helps protect your garden or yard. Below are simple and effective control methods for each.
Gypsy Moth Caterpillar Control
Remove egg masses by scraping them off tree trunks. Use a stick or your fingernail. Destroy the eggs by placing them in soapy water. Handpick caterpillars when you see them. Wear gloves to avoid skin irritation.
Apply Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) spray. Bt is a natural bacteria that kills caterpillars. Spray it on leaves where caterpillars feed. Repeat every few days for best results. Avoid using strong chemicals that harm helpful insects.
Tent Caterpillar Control
Cut and destroy the silk tents early in the season. Use pruners to remove branches with tents. Drop tents into soapy water to kill the caterpillars inside. Check trees regularly for new tents.
Introduce natural predators like birds or parasitic wasps. These insects help control tent caterpillar numbers. Use insecticidal soap spray on tents and caterpillars. Spray directly on the pests for quick control.
Seasonal Activity
Seasonal activity helps identify and control caterpillar pests. Gypsy moth caterpillars and tent caterpillars show different activity times. Understanding these periods can help protect trees effectively.
Gypsy Moth Caterpillar Seasonal Activity
Gypsy moth caterpillars hatch in early spring. They feed for about six weeks, usually from April to June. During this time, they eat many leaves and can cause tree damage. After feeding, they form cocoons and turn into moths in mid-summer.
Tent Caterpillar Seasonal Activity
Tent caterpillars appear in early spring, often a bit earlier than gypsy moths. They build silk tents in tree branches to live and feed. Their feeding period lasts about four to six weeks, typically from March to May. Tent caterpillars leave tents before becoming moths in late spring.
Identification Tips
Identifying the Gypsy Moth caterpillar and the Tent caterpillar helps protect your trees. Each type has clear signs. Spotting these signs early can save your garden from damage.
Appearance And Color Patterns
The Gypsy Moth caterpillar has a hairy body with blue and red dots. Its color is mostly brown or gray. Tent caterpillars are smooth and have a white stripe down their back. Their bodies are usually black or dark brown.
Size And Shape Differences
Gypsy Moth caterpillars grow up to 2.5 inches long. Tent caterpillars are shorter, about 2 inches. Gypsy Moths look thicker and more robust. Tent caterpillars appear slimmer and longer.
Silk Tent Presence
Tent caterpillars live in large silk tents inside tree branches. These tents are easy to see in early spring. Gypsy Moth caterpillars do not build tents. They move freely on leaves and branches.
Feeding Behavior
Gypsy Moth caterpillars feed mostly on oak leaves. Tent caterpillars eat many types of trees. Tent caterpillars eat in groups inside their tents. Gypsy Moth caterpillars feed alone at night.

FAQ: Gypsy Moth Caterpillar Vs Tent Caterpillar
What Are The Main Differences Between Gypsy Moth And Tent Caterpillars?
Gypsy moth caterpillars have hairy bodies and single tents, while tent caterpillars build web-like tents in tree branches.
Which Trees Do Gypsy Moth And Tent Caterpillars Prefer?
Gypsy moths prefer oak and hardwood trees; tent caterpillars favor cherry, apple, and other fruit trees.
How Can I Identify Gypsy Moth Caterpillars Easily?
Look for hairy bodies with blue and red spots along their backs for Gypsy Moth caterpillars.
Do Tent Caterpillars Cause More Tree Damage Than Gypsy Moths?
Gypsy moths usually cause more serious defoliation and damage compared to tent caterpillars.
What Is The Best Way To Control Gypsy Moth And Tent Caterpillars?
Removing tents and using natural predators help control tent caterpillars; pheromone traps work for gypsy moths.
Conclusion
Both gypsy moth and tent caterpillars can harm trees and plants. Gypsy moths eat many leaves and can cause serious damage. Tent caterpillars build web-like tents in branches and feed on leaves too. Knowing their differences helps protect your garden better.
Watch for signs like tents or leaf damage. Act early to keep plants healthy and strong. Understanding these pests makes control easier and more effective. Stay alert and care for your green spaces carefully.

